In today’s competitive business landscape, the role of a preliminary sales strategy in driving business success cannot be overstated. It serves as the foundation for establishing strong customer relationships, understanding market dynamics, and ultimately closing deals that drive revenue growth. Let’s delve into the importance of pre-sales strategy and its impact on overall business success.
What is a Pre-Sales Strategy?
Before diving into the intricacies of pre-sales strategy, it’s essential to grasp its definition, significance, key components, objectives, and how it differs from sales and post-sales strategies.
Pre-sales strategy refers to the set of activities, processes, and methodologies that organizations employ to engage with potential customers before the actual sales transaction takes place. Its significance lies in its ability to lay the groundwork for successful sales outcomes by identifying, nurturing, and qualifying leads, understanding customer needs, and building credibility and trust.
Key Components and Objectives of a Pre-Sales Strategy
The key components and objectives of a pre-sales strategy typically include:
Lead Generation: Identifying and attracting potential leads through various marketing and prospecting efforts.
Lead Qualification: Assessing leads based on criteria such as fit, interest, and readiness to buy, to prioritize sales efforts effectively.
Customer Profiling: Conducting research to understand the needs, preferences, pain points, and buying behaviors of target customers.
Solution Development: Developing customized solutions and proposals that address the specific needs and requirements of potential customers.
Engagement and Education: Engaging with potential customers through meaningful conversations, providing valuable insights and information, and positioning the organization as a trusted advisor.
Objection Handling: Addressing customer objections and concerns effectively to overcome barriers to sales success.
Relationship Building: Establishing and nurturing relationships with potential customers to build credibility, trust, and rapport.
Differentiating from Sales and Post-Sales Strategies
While pre-sales, sales, and post-sales strategies are interconnected and complementary, they serve distinct purposes:
Pre-Sales Strategy: Focuses on activities and processes that occur before the sale, such as lead generation, lead qualification, customer profiling, and solution development.
Sales Strategy: Centers around activities and processes involved in closing deals and generating revenue, such as negotiation, contract signing, and order fulfillment.
Post-Sales Strategy: Involves activities and processes that occur after the sale, such as customer onboarding, support, and relationship management, aimed at ensuring customer satisfaction and retention.
Understanding the unique role and significance of pre-sales strategy is essential for organizations seeking to drive successful sales outcomes and achieve sustainable business growth. It serves as the foundation for building strong customer relationships, understanding market dynamics, and ultimately closing deals that drive revenue and profitability.
Importance of Pre-Sales Strategy in Driving Business Success
The pre-sales phase is where the groundwork for successful sales transactions is laid. It is the crucial period during which potential leads are identified, qualified, and nurtured before they are ready to make a purchasing decision. A well-defined pre-sales strategy is essential for several reasons:
Lead Generation and Qualification: A robust pre-sales strategy enables businesses to identify and qualify leads effectively. By understanding the needs, pain points, and buying behaviors of potential customers, organizations can prioritize their efforts and focus on prospects with the highest likelihood of conversion.
Understanding Customer Needs: Pre-sales activities, such as market research and customer profiling, provide invaluable insights into customer needs and preferences. This knowledge allows businesses to tailor their offerings and messaging to address specific customer challenges and objectives.
Building Credibility and Trust: The pre-sales phase offers opportunities for businesses to establish credibility and trust with potential customers. By providing valuable information, insights, and support during the early stages of the sales cycle, organizations can position themselves as trusted advisors and partners.
Customizing Solutions: A well-executed pre-sales strategy enables businesses to develop customized solutions that meet the unique needs and requirements of each customer. By understanding customer pain points and objectives, organizations can tailor their offerings to deliver maximum value and relevance.
Mitigating Risks: Pre-sales activities help businesses identify potential risks and challenges associated with sales opportunities early on. By conducting thorough due diligence and risk assessment, organizations can proactively address concerns and minimize the likelihood of deal failures.
In essence, a strong pre-sales strategy sets the stage for successful sales outcomes by laying the groundwork for effective lead generation, customer engagement, and solution development. It empowers businesses to understand their customers better, build meaningful relationships, and ultimately drive revenue growth and business success.
The Pre-Sales Process
The pre-sales process is a structured approach that guides organizations through the various stages of engaging with potential customers before the actual sales transaction takes place. Let’s explore the key steps involved:
Identifying and Qualifying Leads
Lead Generation: Utilize various marketing channels, such as inbound marketing, content marketing, and networking events, to attract potential leads.
Lead Qualification: Assess leads based on criteria such as fit, interest, budget, authority, and timeline (BANT), to determine their readiness to buy and prioritize sales efforts effectively.
Researching and Understanding Customer Needs
Market Research: Conduct market research to identify trends, opportunities, and challenges within the target market.
Customer Profiling: Gather information about potential customers, including their industry, company size, pain points, goals, and buying behaviors, to better understand their needs and preferences.
Creating Tailored Solutions and Proposals
Solution Development: Develop customized solutions and proposals that address the specific needs, challenges, and objectives of potential customers.
Value Proposition: Clearly articulate the value proposition of the proposed solution, highlighting the benefits, advantages, and return on investment (ROI) it offers.
Presenting and Demonstrating Value to Prospects
Engagement: Engage with potential customers through meaningful conversations, presentations, and demonstrations, to showcase the value and capabilities of the proposed solution.
Education: Provide valuable insights, information, and resources that help potential customers make informed decisions and understand the benefits of the proposed solution.
Handling Objections and Addressing Concerns
Active Listening: Listen actively to potential customer objections and concerns, acknowledging their validity and seeking to understand the underlying reasons behind them.
Addressing Concerns: Respond to objections with empathy and confidence, providing evidence, data, and testimonials to address potential customer concerns and demonstrate the value and credibility of the proposed solution.
By following these steps and executing the pre-sales process effectively, organizations can identify, engage with, and convert potential leads into satisfied customers, driving revenue growth and business success.
Developing a Pre-Sales Playbook
A pre-sales playbook is a comprehensive guide that outlines standardized processes, roles, responsibilities, and best practices to guide the pre-sales team in effectively engaging with potential customers. Let’s explore the key components of developing a pre-sales playbook:
Creating Standardized Processes and Workflows
Lead Management: Define processes for lead generation, qualification, and tracking to ensure consistency and efficiency in managing potential customer interactions.
Solution Development: Establish standardized procedures for developing customized solutions and proposals, including templates, guidelines, and approval workflows.
Defining Roles and Responsibilities within the Pre-Sales Team
Team Structure: Define the organizational structure of the pre-sales team, including roles such as pre-sales engineers, solution architects, and consultants.
Role Descriptions: Clearly define the responsibilities, expectations, and qualifications required for each role within the pre-sales team to ensure clarity and alignment.
Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Metrics
Lead Conversion Rate: Measure the percentage of leads that are successfully converted into sales opportunities, indicating the effectiveness of lead generation and qualification efforts.
Win Rate: Track the percentage of sales opportunities that result in closed deals, providing insights into the overall effectiveness of the pre-sales process.
Documenting Best Practices and Lessons Learned
Case Studies: Document successful pre-sales engagements as case studies, highlighting key challenges, strategies, and outcomes to serve as learning resources for the pre-sales team.
Continuous Improvement: Encourage ongoing learning and development within the pre-sales team by regularly reviewing and updating the pre-sales playbook based on lessons learned and feedback from sales engagements.
By developing a comprehensive pre-sales playbook that includes standardized processes, clear roles and responsibilities, measurable KPIs, and documented best practices, organizations can empower their pre-sales team to operate more efficiently, effectively, and consistently, ultimately driving better outcomes and achieving business success.
Leveraging Technology in Pre-Sales
In today’s digital age, technology plays a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of pre-sales activities. Let’s explore how organizations can leverage technology to streamline pre-sales processes and drive better outcomes:
Utilizing Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
Lead Management: CRM systems allow organizations to centralize and manage leads effectively, tracking interactions, status changes, and follow-up activities.
Customer Insights: CRM systems provide valuable insights into customer behaviors, preferences, and engagement history, enabling pre-sales teams to tailor their approach and messaging accordingly.
Implementing Account-Based Selling Tools
Account-based selling (ABS) is a targeted sales strategy that focuses on engaging and converting high-value accounts through personalized and tailored interactions. Let’s explore how organizations can implement account-based selling and leverage sales enablement tools effectively:
Identifying Target Accounts: Begin by identifying high-value target accounts that align with your organization’s ideal customer profile (ICP). Utilize data-driven insights and market research to prioritize accounts with the highest potential for revenue growth.
Personalizing Outreach: Tailor your outreach efforts to resonate with the unique needs and challenges of each target account. Leverage account-specific messaging, content, and value propositions to demonstrate your understanding of their business and offer relevant solutions.
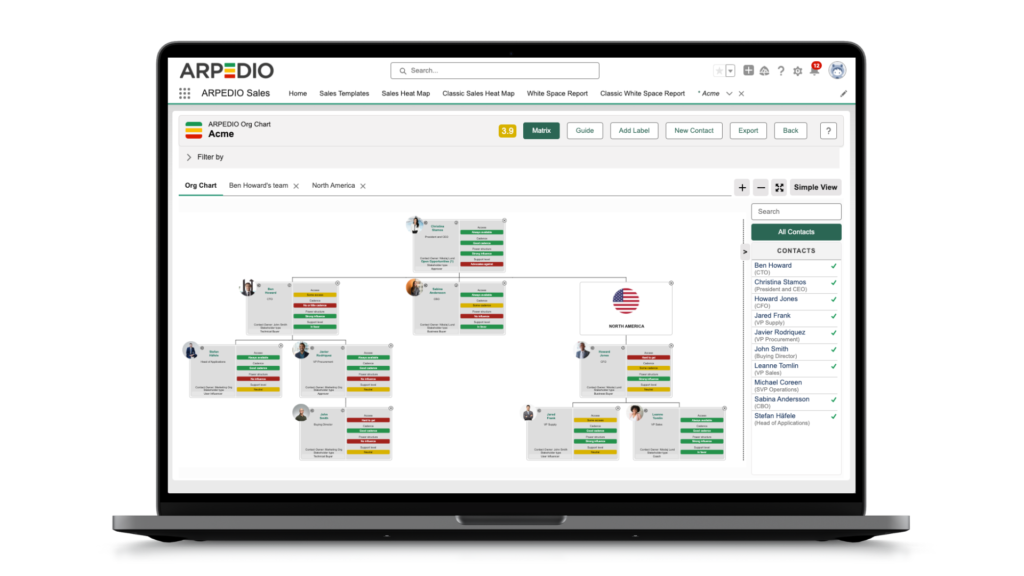
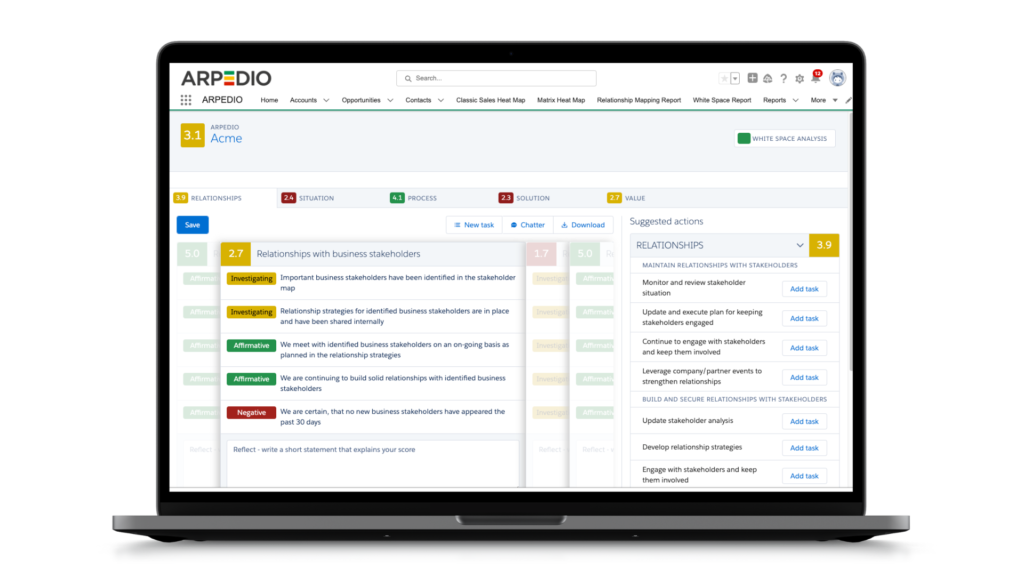
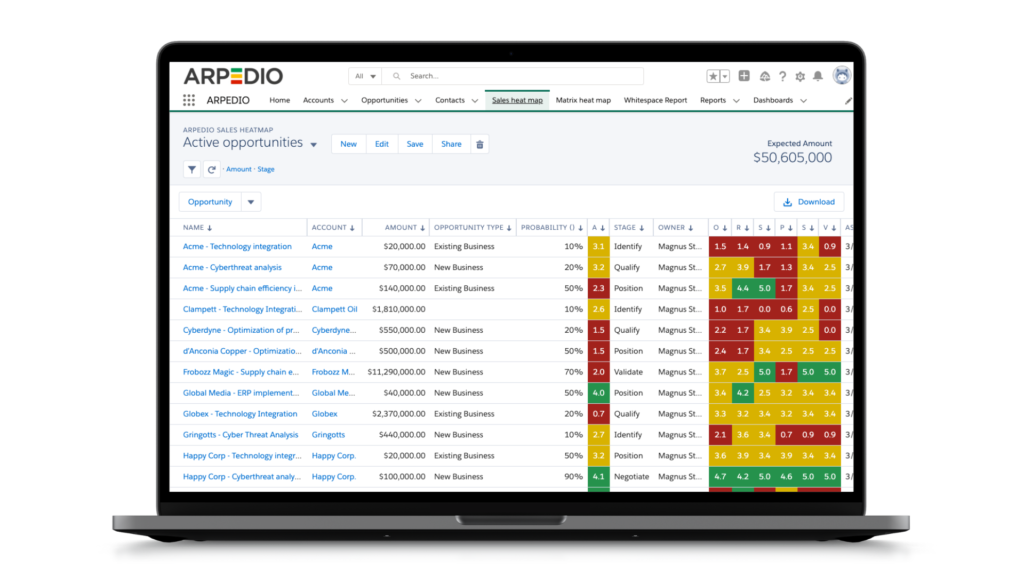
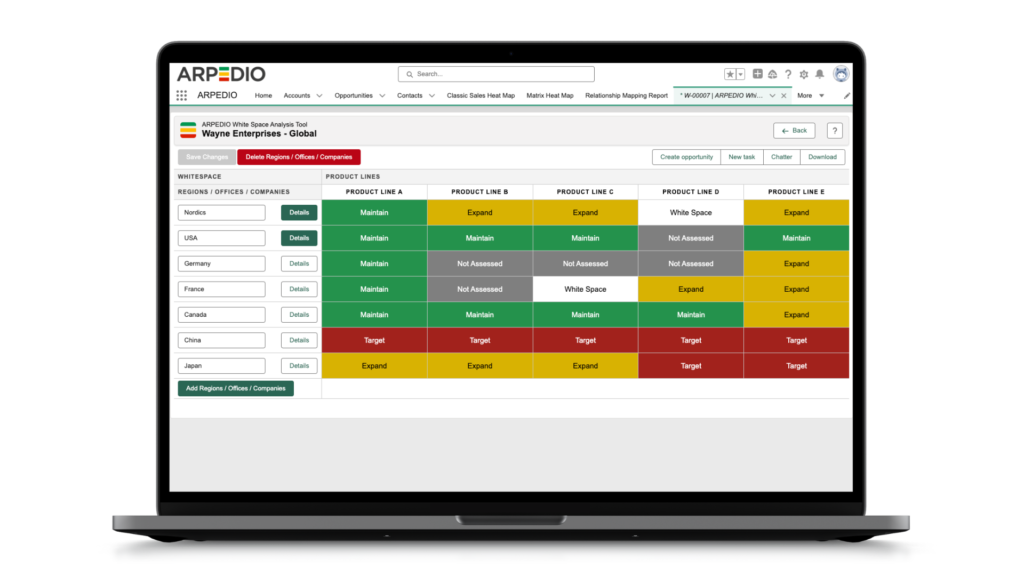
Utilizing Account-Based Selling Tools: Invest in account-based selling tools, such as ARPEDIO. The account-based selling platform offered by ARPEDIO delivers visual organizational charts, heat maps of stakeholder relationships, current account plans, suggested next-best actions, precise weighted pipelines, and white space analysis – all seamlessly integrated within Salesforce.
Segmenting and Targeting: Segment your target accounts based on various criteria, such as industry, company size, and buying stage, to personalize your approach and deliver tailored solutions. Leverage sales enablement tools to track account engagement and prioritize follow-up activities.
Collaborating Across Teams: Foster collaboration between sales, marketing, and customer success teams to ensure alignment and coordination in executing account-based selling initiatives. Utilize account-based selling tools to share insights, collaborate on account strategies, and track progress collaboratively.
Measuring and Iterating: Continuously measure the effectiveness of your account-based selling efforts using key performance indicators (KPIs) such as account engagement, conversion rates, and revenue generated. Leverage analytics features in account-based selling tools to gain insights into what’s working and identify areas for improvement.
By implementing account-based selling tools effectively, organizations can drive better alignment with target accounts, deliver personalized experiences, and ultimately achieve higher conversion rates and revenue growth.
Pre-Sales Team Training and Development
Investing in the training and development of the pre-sales team is essential for ensuring they have the knowledge, skills, and capabilities to effectively engage with potential customers and drive successful outcomes. Let’s explore key aspects of pre-sales team training and development:
Providing Product and Industry Knowledge
Product Training: Equip pre-sales professionals with in-depth knowledge of the organization’s products or services, including features, benefits, use cases, and competitive differentiation.
Industry Insights: Provide training on industry trends, market dynamics, and competitive landscape to enable pre-sales teams to better understand customer needs and position solutions effectively.
Developing Consultative Selling Skills
Understanding Customer Needs: Train pre-sales professionals to listen actively, ask probing questions, and uncover customer pain points and objectives to identify opportunities for value-added solutions.
Solution Alignment: Teach pre-sales teams to align proposed solutions with customer needs and objectives, focusing on delivering value and addressing specific challenges.
Conducting Role-Playing Exercises and Simulations
Scenario-Based Training: Conduct role-playing exercises and simulations that replicate real-world sales scenarios, allowing pre-sales professionals to practice and refine their skills in a safe and supportive environment.
Feedback and Coaching: Provide constructive feedback and coaching during role-playing exercises to help pre-sales teams identify areas for improvement and develop confidence in their abilities.
Offering Ongoing Coaching and Support
Continuous Learning: Encourage a culture of continuous learning and development within the pre-sales team, providing access to resources, workshops, and training programs to support skill enhancement and career growth.
Mentorship: Pair pre-sales professionals with experienced mentors who can provide guidance, advice, and support as they navigate their roles and responsibilities.
By prioritizing pre-sales team training and development, organizations can ensure their teams are equipped with the knowledge, skills, and confidence to effectively engage with potential customers, drive value-added conversations, and ultimately contribute to business success.
Challenges and Solutions in Pre-Sales
The pre-sales process presents various challenges that organizations must overcome to drive successful outcomes. Let’s explore some common challenges and potential solutions:
Overcoming Lead Qualification Challenges
Inaccurate or Incomplete Information: Lead qualification can be challenging when information about potential leads is inaccurate or incomplete.
Solution: Implement lead scoring mechanisms and automated lead qualification processes to prioritize leads based on predefined criteria such as fit, interest, and readiness to buy.
Addressing Customization and Scalability Issues
Customization Requirements: Meeting the diverse needs and preferences of potential customers can pose challenges in terms of customization.
Solution: Develop standardized templates, tools, and processes for solution customization, ensuring flexibility and scalability while maintaining consistency and quality.
Managing Time and Resource Constraints
Limited Time: Pre-sales teams often face time constraints when engaging with multiple leads and managing competing priorities.
Solution: Prioritize leads based on their potential value and alignment with organizational objectives, allocating resources and efforts strategically to maximize impact and efficiency.
By proactively addressing these challenges and implementing appropriate solutions, organizations can enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of their pre-sales efforts, driving better outcomes and achieving business success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a well-executed pre-sales strategy is essential for organizations seeking to drive successful outcomes, build meaningful relationships with potential customers, and ultimately achieve business success. By prioritizing activities such as lead qualification, customer engagement, solution development, and team training and development, organizations can lay the groundwork for effective sales engagements and drive revenue growth.
Despite the challenges inherent in the pre-sales process, such as lead qualification challenges, customization and scalability issues, and time and resource constraints, organizations can overcome these obstacles by implementing proactive strategies and solutions.
By leveraging technology effectively, investing in pre-sales team training and development, and proactively addressing common challenges, organizations can streamline pre-sales processes, enhance customer engagement, and drive better outcomes. Ultimately, a well-defined pre-sales strategy serves as the foundation for successful sales transactions, enabling organizations to achieve their business objectives and thrive in today’s competitive marketplace.